Subtotal 0 ₫
Introduction

3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has revolutionized the way we create and manufacture objects. This technology allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects from a digital model by layering materials such as plastics, metals, or resins. The process has opened up new possibilities in various industries, from healthcare to aerospace, and continues to evolve at a rapid pace.
The History of 3D Printing
The concept of 3D printing dates back to the 1980s when it was initially known as rapid prototyping. The first 3D printers were large and expensive, primarily used by companies to develop prototypes quickly and accurately. Over the years, advancements in technology have made 3D printing more accessible and affordable, leading to its widespread adoption across different sectors.
How 3D Printing Works
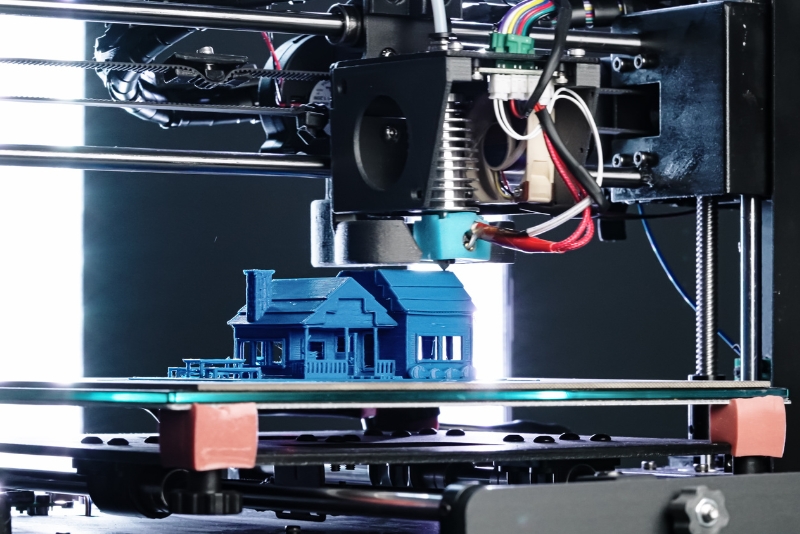
3D printing begins with a digital model created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This model is then sliced into thousands of horizontal layers using slicing software. The 3D printer reads these layers and deposits material layer by layer to build the final object. The most common file format for 3D printing is G-code, which contains the coordinates to guide the printer’s movements.
There are various types of 3D printing technologies, each with its own unique process. Some of the most common methods include:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This method involves melting and extruding thermoplastic filament to create each layer.
- Stereolithography (SLA): This technique uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid layers.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): This process involves using a laser to fuse powdered material into solid layers.
Applications of 3D Printing
The versatility of 3D printing has led to its adoption in numerous industries. In healthcare, 3D printing is used to create custom prosthetics, implants, and even bioprinted tissues and organs. The aerospace industry utilizes 3D printing to produce lightweight and complex components for aircraft and spacecraft. Additionally, the automotive industry benefits from 3D printing by creating prototypes, tools, and end-use parts.
3D printing has also made its way into the fashion and art worlds, allowing designers and artists to create intricate and unique pieces. In construction, 3D printing is being explored for building houses and other structures, offering a faster and more cost-effective alternative to traditional methods.
Advantages of 3D Printing

One of the main advantages of 3D printing is its ability to produce complex and customized objects with minimal waste. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve cutting away material, resulting in significant waste. In contrast, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, using only the necessary amount of material.
Another benefit is the speed and efficiency of 3D printing. Prototyping and production processes that once took weeks or months can now be completed in a matter of hours or days. This rapid turnaround time allows for faster innovation and reduces time-to-market for new products.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many advantages, 3D printing also faces several challenges and limitations. One of the main issues is the limited range of materials that can be used in the process. While advancements are being made, the selection of materials suitable for 3D printing is still relatively small compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Another challenge is the quality and durability of 3D-printed objects. While 3D printing is excellent for prototyping and small-scale production, it may not always meet the standards required for mass production. Additionally, the cost of 3D printers and materials can be prohibitive for some businesses and individuals.
The Future of 3D Printing

The future of 3D printing looks promising, with continued advancements in technology and materials. Researchers are exploring new ways to improve the speed, accuracy, and capabilities of 3D printers. The development of more sustainable and eco-friendly materials is also a key focus, addressing concerns about the environmental impact of 3D printing.
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, it is expected to play an even more significant role in various industries. From personalized healthcare solutions to innovative construction methods, the possibilities are endless. The ongoing innovation in 3D printing will undoubtedly shape the future of manufacturing and design.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing has transformed the way we create and manufacture objects, offering numerous advantages over traditional methods. Its applications span across various industries, from healthcare to aerospace, and continue to expand as technology advances. While there are challenges and limitations to overcome, the future of 3D printing holds immense potential for innovation and growth. As we continue to explore the possibilities of this groundbreaking technology, it will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of manufacturing and design.


🛎 You Have A Message # 512309. Read > Https://telegra.ph/Binance-Support-02-18?hs=5c4fb85cc8e50deddd5d751944cfc80e& 🛎
jqphyq
📔 + 0.75723162 BTC.GET - Https://telegra.ph/Binance-Support-02-18?hs=5c4fb85cc8e50deddd5d751944cfc80e& 📔
6k6y6j